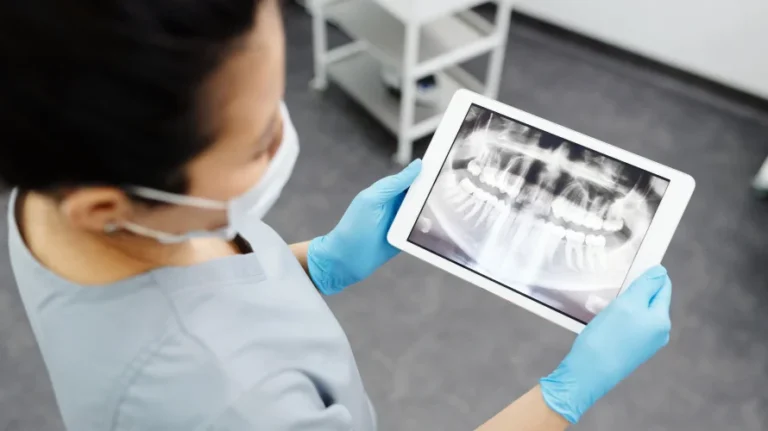
What is Oral Diagnosis and Radiology
The Oral Diagnosis and Radiology Clinic is where we first welcome our patients. It is the clinic that diagnoses diseases of the mouth, teeth, and mucosa using adjunctive examination methods, prepares the most appropriate treatment plan for the healing of these tissues, and directs patients to the specialty departments where their treatment will be performed.
We strive to provide service to our patients using modern dentistry and radiology equipment.
Patients who come to our center are examined by our oral diagnosis physician in the oral diagnosis clinic before starting their treatment based on their complaints. If deemed necessary, they are directed to the radiology clinic for radiographs, and a personalized treatment plan is prepared for them in the most detailed manner.
WHY IS A GOOD EXAMINATION NECESSARY?
In the first stage of the examination, patients are asked if they have any problems with their general health or any diseases that require them to be under constant medical supervision. A detailed inquiry into this general medical history is very important for the dentist to take necessary precautions against complications that may arise during our patients’ dental treatments. The procedures to be performed and the medications to be used during treatments are arranged in accordance with our patients’ health, based on this information obtained during the examination.
In the second stage of the examination, the necessary radiographs are requested from our patients. After the radiological examination is completed by our oral diagnosis physician, the best treatment plan for the patient is determined. Various alternatives for this treatment plan are explained to our patients in detail, along with their advantages and disadvantages.
Treatments started without a good examination and treatment plan will not only be unsuccessful and not long-lasting but can also cause health, time, and financial losses for the patient.
In our center, the extraoral and intraoral examinations of our patients are performed using the necessary technology for diagnosis.
The patient is informed about the treatment plan created as a result of these examinations, and the patient is asked to sign the “General Information and Consent Form.” Our patients who sign this form are then directed to the relevant clinics.
WHAT TO PAY ATTENTION TO DURING AN EXAMINATION AND RADIOGRAPHY?
During the Examination;
The questions asked should be answered correctly.
It should not be forgotten that incomplete information will jeopardize the patient’s health and treatment.
In the Radiology Clinic;
Before the radiograph is taken, all metal jewelry in the head and neck area (glasses, hearing aids, hair clips, earrings, necklaces, nose studs, piercings, etc.) must be removed. If there are any removable (mobile) prostheses in the mouth, they must also be taken out.
1- Digital Panoramic X-ray This is a type of X-ray that displays all the teeth and the jawbone together using less radiation. It is especially used for general oral examinations for control purposes and for simple surgical procedures such as impacted tooth extraction, resection, small cysts, or the placement of a few implants. Being digital increases the image quality and significantly reduces the amount of radiation the person receives.
2- Digital Radiographs (RVG) Cavities and problems in the root canal that cannot be detected during the examination can be easily identified with the help of X-rays. The images can be viewed instantly on a computer screen, and desired color adjustments, magnification/reduction operations, and measurements can be made on them. The images can be stored in the patient’s file in a computer environment and can be shared online when necessary. The radiation dose the patient is exposed to is also significantly reduced.
3- Computed Tomography (CT) With this method, cross-sectional images of the oral region can be obtained, allowing the relationships of teeth or pathological formations with surrounding tissues to be examined in all three planes. It is a radiological diagnostic method that allows for the cross-sectional examination of the desired area using X-rays. In cases involving large cysts, tumors, and the planning of multiple implant applications, the horizontal bone thickness, the positions of the sinus cavities, and the paths of nerves and blood vessels can be determined precisely. This minimizes the risk of surgical procedures.
CAN I HAVE A RADIOGRAPH TAKEN WHILE PREGNANT?
Although the amount of radiation emitted by radiography devices used in dentistry is very low and not at a level to threaten human health, radiographs are not taken from pregnant women or those who suspect they might be pregnant, except in cases of urgent medical indication and a doctor’s request. However, if absolutely necessary, a radiograph can be taken. Unnecessary radiographs should be avoided.
Pregnant women must wear a lead apron when entering the radiology clinic.
IS THE X-RAY USED IN DENTAL RADIOLOGY HARMFUL?
The amount of radiation you receive during a panoramic radiograph is synthetic radiation, not radon from radioactive materials used in nuclear technologies. It is equivalent to the amount you would receive from sitting in front of a computer for 4 hours or walking outside on a sunny day.
The lead vest that should be worn when taking a radiograph prevents other organs and tissues from receiving unnecessary X-rays. This precaution is a general rule of radiology.
WHAT IS LOCAL ANESTHESIA?
A wide variety of anesthesia types can be administered to you during your treatments. For minor dental treatments, local anesthesia, conscious sedation, and general anesthesia can be applied. Local anesthesia is a form of treatment that affects the nerves of the tooth and surrounding tissues to prevent pain. If you have a history of allergies, or if you have heart disease, blood disorders, high blood pressure, or any other general health condition, you must inform your dentist.
During and after the application of local anesthesia, pain, swelling, burning, infection, temporary or permanent nerve damage, and unexpected allergic reactions may develop. Allergic reactions can manifest as itching, rash, nausea, vomiting, difficulty breathing, an increase (tachycardia) or decrease (bradycardia) in heart rate, and, in very rare instances, death. Since local anesthesia will be administered, do not consume alcohol, drugs, or other similar substances before treatment. Do not drive a vehicle after treatment with local anesthesia. For conscious sedation and general anesthesia applications, please carefully read the Patient Consent Form that will be given to you separately in the relevant clinics!