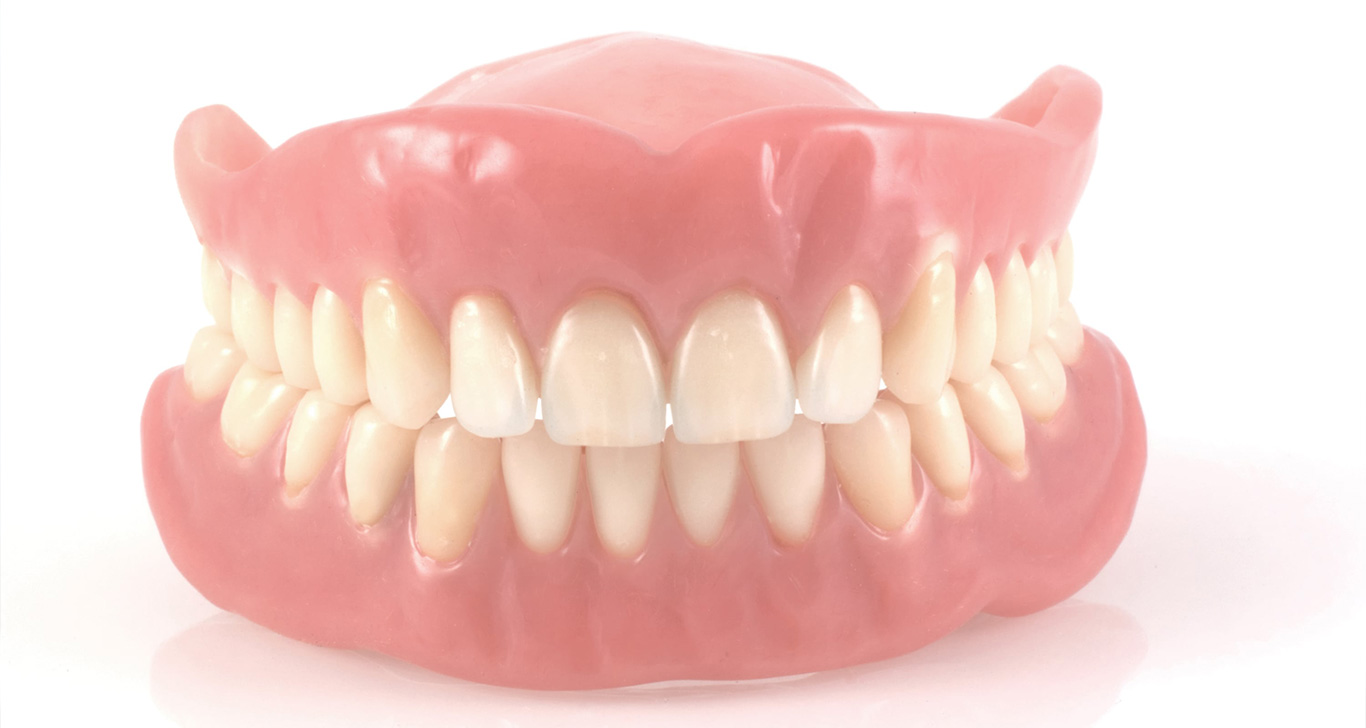
PROSTHODONTICS (PROSTHETIC DENTISTRY)
Teeth and oral tissues can be lost for various reasons. Prostheses are prepared using various materials to replace them. The patient’s chewing and speech functions, aesthetics, comfort, and health are restored. This includes different types of prostheses such as fixed, removable partial, removable complete, and implant-supported prostheses. Additionally, disorders of the temporomandibular joints (jaw joints) and their treatment are evaluated and managed within the scope of prosthetic dentistry.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a dental prosthesis?
A dental prosthesis is an artificial tooth or set of teeth made to fill the space of missing teeth and to restore functions such as chewing and speech. There are two main types: fixed and removable.
What is the difference between fixed and removable prostheses?
Fixed prostheses are permanently placed in the mouth and cannot be removed by the patient (e.g., bridges or implant-supported prostheses).
Removable prostheses, on the other hand, can be inserted and taken out by the patient (e.g., full dentures or partial dentures).
Is getting a dental prosthesis painful?
Generally, no pain is felt during the prosthesis application. However, mild discomfort may be experienced during the adjustment period with a new prosthesis. This is temporary and will decrease over time.
How long does it take to make a prosthesis?
While it varies depending on the type of prosthesis, it is usually completed in a few sessions. The processes of preparation, taking impressions, try-ins, and final delivery can take 1-3 weeks.
How do you get used to a dental prosthesis?
In the first few days, you may experience difficulty speaking and a feeling of fullness in your mouth. With regular use and patience, this feeling will pass over time. If necessary, your dentist can make minor adjustments.